Schedule jobs #
Starburst Galaxy provides several ways to perform maintenance tasks on a set schedule:
- From the Jobs menu:
- SQL jobs to run SQL statements on a schedule.
- Materialized view refresh jobs.
- Other maintenance jobs:
- Data maintenance jobs for object storage catalogs only.
- Data classification jobs to automatically apply classify table data in order to apply attribute tags.
SQL jobs #
SQL job scheduling is best suited for executing SQL statements, such as
CREATE, DROP, REFRESH, MERGE and TRUNCATE. Statements that return
results are not supported, which excludes statements that begin with SELECT;
however, using SELECT as part of a statement is supported.
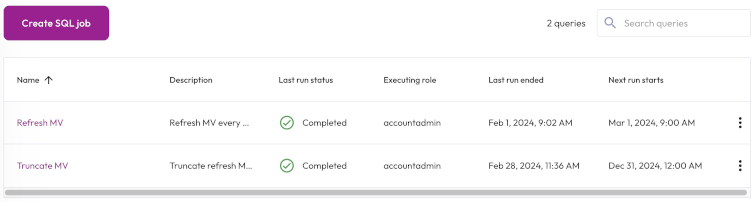
In the navigation menu, click Jobs. The SQL tab is where you create, view, search for, and manage SQL jobs.
The SQL jobs list is organized in the following columns:
- Name: The name of the SQL job. Click the column heading to sort in ascending or descending alphabetical order.
- Description: The description provided for the SQL job.
- Last run status: When the SQL job was last run.
- Executing role: The role running the SQL job.
- Last run ended: The date and time the last SQL job run ended.
-
Next run starts: The next date and time the SQL job is scheduled to start running. If the schedule is paused, the status of the schedule also appears here.
Create a SQL job #
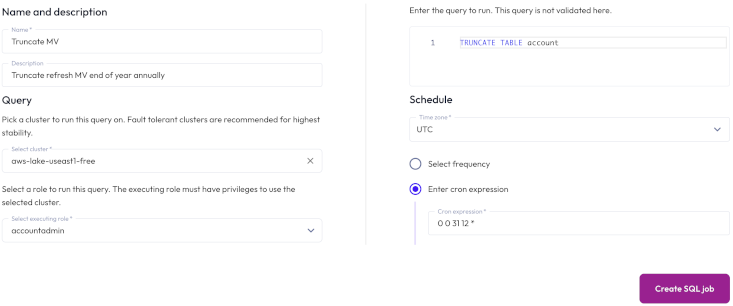
To run a statement on a recurring schedule, click Create SQL job, then provide the following information in the Create SQL Job dialog:
-
In the Name and description section, enter a name for the job and a useful description.
-
In the Query section, enter the statement you want to run.
-
In the Execution details section:
-
Expand the first drop-down menu, and select a role to run the statement. The role must have the Manage Security privilege.
-
In the Select cluster field, choose a cluster to run the statement on. We recommend using a fault tolerant cluster.
-
-
In the Job schedule section:
-
Choose the time zone of your operating system from the drop-down menu.
-
Choose the Select frequency or Enter cron expression recurring interval format.
For Select frequency: Choose an hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, or annual schedule from the drop-down menu. The corresponding values depend on the schedule selected:
- Hourly: Enter a value between 1 minute and 59 minutes.
- Daily: Enter a time in the format
hh:mm, then specify AM or PM. - Weekly: Enter a time in the format
hh:mm, specify AM or PM, then select a day of the week. - Monthly: Enter a time in the format
hh:mm, specify AM or PM, then select a date. - Annually: Enter a month, day, hour, and minutes in the format
MM/DD hh:mm. Specify AM or PM.
For Enter cron expression: Enter the desired schedule in the form of a cron expression. For example, a SQL job run weekly at 9:30 AM on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday:
-
30 9 * * 1,3,5
-
Click Save.
View SQL job details #
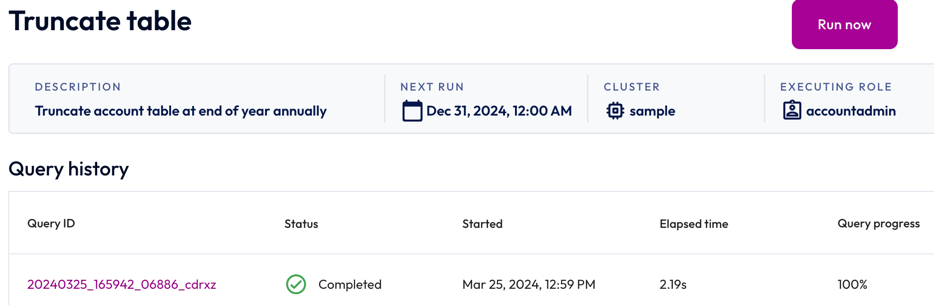
To view the details of a SQL job, click the name of the job. The header of the Job details pane displays the following information about your SQL job:
- Description: The description provided for the SQL job.
- Next run: The next date and time the SQL job is scheduled to run. If the schedule is paused, the status of the schedule also appears here.
- Cluster: The chosen cluster.
- Executing role: The role running the SQL job.
Run now allows you to run the SQL job instantly.
Completed statements and statements in progress appear in the Job history section, which displays the following information:
- Query ID: A unique identifier for each statement. Click the Query ID to view statement details.
- Status: check_circle for successfully completed statements and close for failed statements.
- Started: Date and time the statement started running.
- Elapsed time: Total duration for processing the statement.
- Query progress: How much of the process is completed; shown as a percentage.
To see statement details, click the Query ID.
Manage SQL jobs #
You can manage SQL jobs in the SQL jobs pane and Job details pane. Click themore_vertoptions menu to edit, delete, pause, or resume the selected SQL job.
MV refresh jobs #
Materialized view refresh is only available for object storage catalogs. Your role must also have
In the navigation menu, click Jobs. The Materialized view refresh tab is where you view, search for, and manage materialized view refresh jobs.
All of the materialized view refresh jobs you create are displayed in a list with the following information:
- Job name: The name of the materialized view refresh job. Click the column heading to sort in ascending or descending alphabetical order.
- Last run status: When the materialized view refresh job was last run.
- Executing role: The role running the materialized view refresh job.
- Last run ended: The date and time the last materialized view refresh job run ended.
- Next run starts: The next date and time the materialized view refresh job is scheduled to start running. If the schedule is paused, the status of the schedule also appears here.
Create a MV refresh job #
You can create a materialized view refresh job by using the Create materialized view refresh job dialog or by running a SQL statement in the query editor.
To use the dialog, click Create materialized view refresh job, then provide the following information:
-
In the Materialized view section, select a catalog, schema, and materialized view.
-
In the Execution details section:
-
Expand the first drop-down menu, and select a role to run the statement. The role must have the Manage Security privilege.
-
In the Select cluster field, choose a cluster to run the statement on. We recommend using a fault tolerant cluster.
-
-
In the Job schedule section:
-
Choose the time zone of your operating system from the drop-down menu.
-
Choose the Select frequency or Enter cron expression recurring interval format.
For Select frequency: Choose an hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, or annual schedule from the drop-down menu. The corresponding values depend on the schedule selected:
- Hourly: Enter a value between 1 minute and 59 minutes.
- Daily: Enter a time in the format
hh:mm, then specify AM or PM. - Weekly: Enter a time in the format
hh:mm, specify AM or PM, then select a day of the week. - Monthly: Enter a time in the format
hh:mm, specify AM or PM, then select a date. - Annually: Enter a month, day, hour, and minutes in the format
MM/DD hh:mm. Specify AM or PM.
For Enter cron expression: Enter the desired schedule in the form of a cron expression. For example, a SQL job run weekly at 9:30 AM on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday:
-
30 9 * * 1,3,5
- Click Save.
To create a materialized view refresh job using a SQL statement, go to the query editor.
Write a statement using CREATE MATERIALIZED
VIEW that includes
the refresh_schedule property. The refresh_schedule property must be set
with the frequency of the refresh as a cron expression:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW my_refresh_materialization
WITH (
refresh_schedule = '0 0 1 * *'
) AS
SELECT *
FROM lakehouse.burst_bank.customer;
The job scheduler is set to the UTC time zone by default. To ensure your new refresh job runs as scheduled, complete the following steps:
- Locate the materialized view refresh job in the jobs list.
- Click themore_vertoptions menu, and select Edit job.
- Expand the Time zone drop-down menu, and select the time zone of your operating system.
View MV refresh job details #
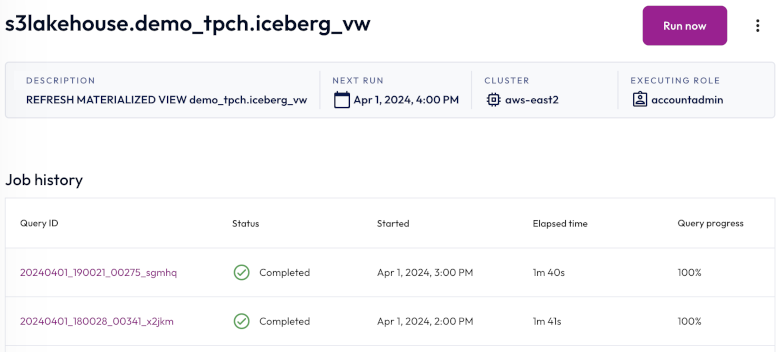
To view the details of a materialized view refresh job, click the name of the job. The header of the Job details pane displays the following information about your materialized view refresh job:
- Description: A read-only, auto generated description for the materialized view refresh job.
- Next run: The next date and time the materialized view refresh job is scheduled to run. If the schedule is paused, the status of the schedule also appears here.
- Cluster: The chosen cluster.
- Executing role: The role running the materialized view refresh job.
Run now allows you to run the materialized view refresh job instantly.
Completed statements and statements in progress appear in the Job history section, which displays the following information:
- Query ID: A unique identifier for each statement. Click the Query ID to view statement details.
- Status: check_circle for successfully completed statements and close for failed statements.
- Started: Date and time the statement started running.
- Elapsed time: Total duration for processing the statement.
- Query progress: How much of the process is completed; shown as a percentage.
To see statement details, click the Query ID.
Manage MV refresh jobs #
You can manage materialized view refresh jobs in the Materialized view refresh jobs pane, the Job details pane, and the query editor.
To edit, delete, pause, or resume the selected SQL job, click themore_vertoptions menu.
To make changes to a materialized view refresh job in the query editor, use the ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW statement.
To drop a materialized view refresh job, use the DROP MATERIALIZED
VIEW statement. To
remove a refresh job from a materialized view without dropping it, set the
refresh_schedule property to DEFAULT.
MV refresh job permissions #
Your active role set determines which materialized view refresh jobs you can access.
The accountadmin role cannot access all refresh jobs by default. To grant
accountadmin access to the jobs created by another role, you must grant that
role to accountadmin using the following command:
GRANT <role_name> TO accountadmin;
Data maintenance jobs #
For object storage catalogs only, you can run table maintenance tasks that improve performance and reduce storage.
For more information, use the following links:
Data classification jobs #
You can automatically classify data in catalogs, schemas, tables, or views in order to apply attribute tags to that data.
For details, see Automatic data tagging.
Is the information on this page helpful?
Yes
No